
Cyclone-battered region sees storm Dikeledi leave Mayotte for Mozambique
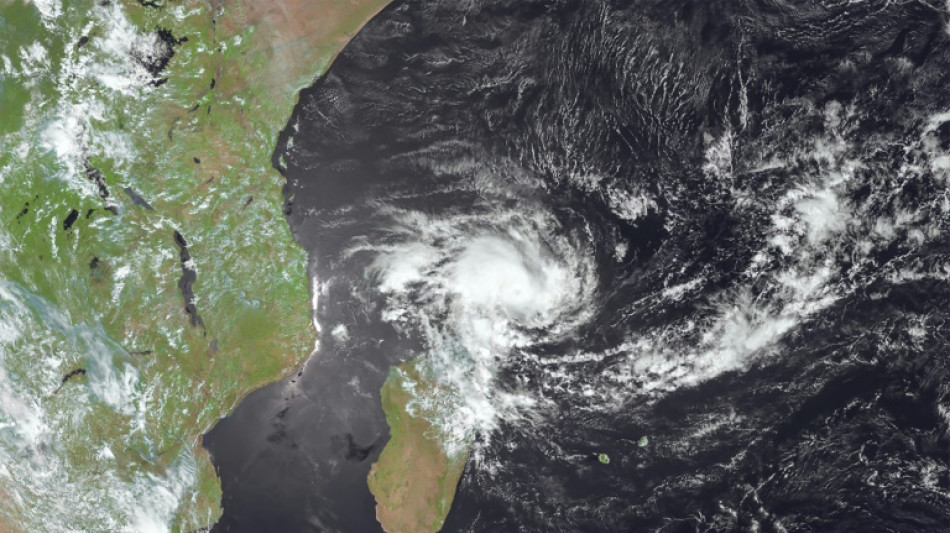
Tropical storm Dikeledi barrelled towards Mozambique on Monday after leaving three dead in Madagascar and triggering floods in the French territory of Mayotte, less than a month after the cyclone-battered region was hit by Chido.
It had hit Madagascar's northern tip as a cyclone Saturday, whipping up strong winds and torrential rains.
The storm left at least three dead, according to the National Office for Risk and Disaster Management on Sunday.
By Sunday, Dikeledi had weakened into a severe tropical storm, passing Mayotte -- France's poorest department -- by about 100 kilometres (60 miles) at its closest point.
Mayotte's prefect Francois-Xavier Bieuville said the red alert -- imposed since Saturday -- would remain in place at least until nightfall.
"We have a territory that is very fragile so I decided to keep this red alert," Bieuville, the top Paris-appointed official on Mayotte, said on television.
"We still have extremely strong winds and rainfall that is just as strong."
However, no casualties have been reported from the storm, he said.
Diekledi came as the region was still reeling from the deadly Cyclone Chido.
It left at least 39 dead in Mayotte, injuring more than 5,600, and causing colossal damage.
When Chido made landfall in the southeast African country of Mozambique in December, it inflicted a more punishing toll -- killing at least 120 people and injuring more than 900.
By Monday morning around 0200 GMT, Dikeledi was 150 kilometres off the coast of Mozambique, according to French weather administration Meteo-France.
It is expected to intensify over the warm waters of the Mozambique Channel to reach "the stage of an intense or very intense tropical cyclone", Meteo-France said.
- 'Loss for words' -
Despite the storm's passage, heavy rains were still expected Monday in Mayotte, Floriane Ben Hassen of Mayotte's meteorological centre said on television, recommending "great caution in all coastal villages... around these high tide peaks".
About a dozen houses in the south and the centre of the archipelago had been washed away, according to local emergency services Sunday, while several villages had been inundated, including Mbouini, on the southern coast.
"We're traumatised by everything that happened here. We've already been traumatised Chido, and now we're at a loss for words," Massa, a resident of Mbouini who did not provide her full name, told AFP.
"We're only in the middle of the rainy season, so we don't know what's going to happen between now and February or March," she said.
Due to the red alert -- which banned all travel except for rescue services and other authorised personnel -- Mayotte's inhabitants have been confined to their homes since Saturday until further notice.
More than 4,000 people have been mobilised in Mayotte, including members of the police and the military, while France's overseas territory minister told AFP that 80 accommodation centres were set up to host 14,500 people.
As Dikeledi approaches Mozambique, its Nampula region "should experience very degraded conditions" on Monday, Meteo-France said, warning of torrential rainfall and "very destructive winds", as well as dangerous sea conditions.
Cyclones usually develop in the Indian Ocean from November to March. This year, surface water temperatures are close to 30 degrees Celsius (86 Fahrenheit) in the area, which provides more intensity to storms, a global warming phenomenon also observed in the North Atlantic and the Pacific.
P.Rossi--IM



